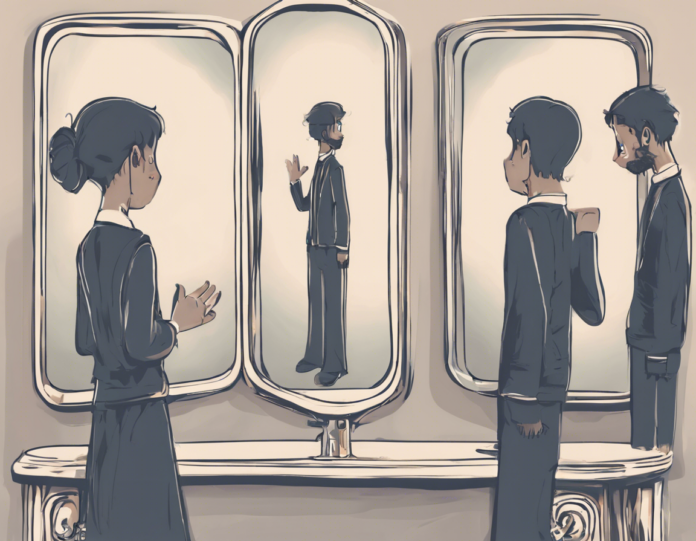
Introduction
The fascination with mirrors dates back thousands of years – from their early beginnings as polished stones to the elaborate decorative pieces we see today. But beyond their practical use for grooming and self-reflection, mirrors have also captured our imagination with their mysterious qualities and optical illusions. One such intriguing phenomenon is the Mirror Illusion, where our perception of reality seems to be distorted by the reflective surface. In this article, we will delve into the science behind this phenomenon, explore how our brain processes mirror images, and uncover some of the most famous mirror illusions throughout history.
How Do Mirrors Work?
Before we can understand the Mirror Illusion, we must first grasp the basics of how mirrors work. A mirror is essentially a smooth, highly reflective surface that reflects light without scattering it. When light hits the surface of a mirror, it bounces off at the same angle it hit the mirror, following the principle of reflection. This process creates an image that appears to be located behind the mirror, giving us the illusion of depth.
The Mirror Illusion Explained
The Mirror Illusion occurs when our brain processes the reflected image in a way that can be deceiving or misleading. This phenomenon is due to a combination of factors, including our brain’s interpretation of visual cues, our past experiences, and our expectations of how objects should appear. When we look into a mirror, our brain automatically tries to make sense of the reflected image by comparing it to our stored memory of how we look. This can sometimes lead to discrepancies between reality and what we see in the mirror, creating the illusion that our reflection is distorted or altered.
Common Mirror Illusions
1. The Two-Faced Illusion: One of the most famous mirror illusions is the two-faced illusion, where a person’s reflection appears to have two different expressions simultaneously. This phenomenon is often used in psychology studies to show how our perception of emotions can be influenced by subtle cues.
2. The Mirror Box Illusion: In this illusion, objects placed inside a specially constructed mirrored box appear to be duplicated and rearranged in a mesmerizing and confusing way. This optical illusion plays tricks on our sense of spatial awareness and depth perception.
3. The Infinity Mirror Effect: By placing two mirrors facing each other, an infinity mirror effect is created, where reflections bounce back and forth in a seemingly endless loop. This mesmerizing visual trick is a favorite in art installations and interior design.
4. The Mirror Hand Illusion: By placing a hand behind a mirror and moving it in sync with a visible hand in front of the mirror, a sensation of an extra limb can be induced. This illusion demonstrates how our brain can be tricked into perceiving additional body parts.
5. The Mirror Amnesia Illusion: In this illusion, participants are asked to read a list of words while looking at their reflection in a mirror. After a few minutes, when asked to recall the words, some participants may struggle or fail to remember them due to the interference caused by the mirror image.
The Brain and Mirror Neurons
One of the key factors in how we perceive mirror illusions is the role of mirror neurons in our brain. Mirror neurons are a type of brain cell that activates both when we perform an action and when we observe someone else performing the same action. This mirroring effect is thought to be crucial for learning, empathy, and understanding the intentions of others. When we look at our reflection in a mirror, mirror neurons may play a role in how we recognize ourselves and interpret the reflected image.
The Psychological Impact of Mirror Illusions
Mirror illusions can have various psychological effects on individuals, ranging from amusement and curiosity to confusion and discomfort. For some people, experiencing mirror illusions can challenge their sense of self and reality, leading to existential questioning or altered perceptions of their appearance. On the other hand, mirror illusions can also be a source of entertainment and creative inspiration, prompting artists and designers to explore new ways of using mirrors in art and visual effects.
Practical Applications of Mirror Illusions
Beyond their entertainment value, mirror illusions have practical applications in various fields, including psychology, neuroscience, and visual arts. By studying how mirror illusions affect our perception and cognition, researchers can gain valuable insights into the workings of the human brain and sensory system. In therapy, mirror illusions are used in treatments such as mirror therapy for phantom limb pain or body image disorders. In art and design, mirror illusions are employed to create visually stunning effects and evoke emotional responses from viewers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Are mirror illusions the same as optical illusions?
A1: While mirror illusions are a type of optical illusion, they specifically involve the reflection of light on a mirror surface to create deceptive or misleading images.
Q2: Can mirror illusions be harmful to our perception of reality?
A2: Mirror illusions are generally harmless and temporary, although they can sometimes challenge our perception and cognitive processing. However, they are a natural byproduct of how our brain interprets visual information.
Q3: How can mirror illusions be used in therapeutic settings?
A3: Mirror illusions like mirror therapy are utilized in rehabilitation treatments to alleviate pain, improve motor function, and enhance body awareness in patients with neurological or physical conditions.
Q4: Are there cultural or historical significances associated with mirrors and mirror illusions?
A4: Mirrors hold cultural symbolism in various societies, representing self-reflection, duality, vanity, and supernatural beliefs. Mirror illusions have been used in art and literature throughout history to convey deeper meanings and metaphors.
Q5: Can we train our brain to perceive mirror illusions differently?
A5: While our perception of mirror illusions is largely subconscious and automatic, certain cognitive exercises and perceptual training can help us become more aware of how our brain processes visual information from mirrors.
Conclusion
The Mirror Illusion is a captivating phenomenon that showcases the intricate relationship between our perception, brain function, and the physical properties of mirrors. By exploring the science behind mirror illusions, understanding the role of mirror neurons, and appreciating the diverse applications of mirror effects, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of human cognition and visual processing. Next time you find yourself in front of a mirror, take a moment to ponder the reflection staring back at you – it may just hold more mysteries than meets the eye.